
Do you often feel drained or sluggish? Your protein intake could be the hidden culprit. Daily fatigue is a common issue for many men.
| Age Group | Percentage Reporting Fatigue/Exhaustion |
|---|---|
| All Men | Approximately 10% |
| Men aged 18-44 | About 11% |
| Men older than 45 | Under 10% |
Protein matters for your energy and overall health. Yet, a surprising number of men have a suboptimal protein intake.
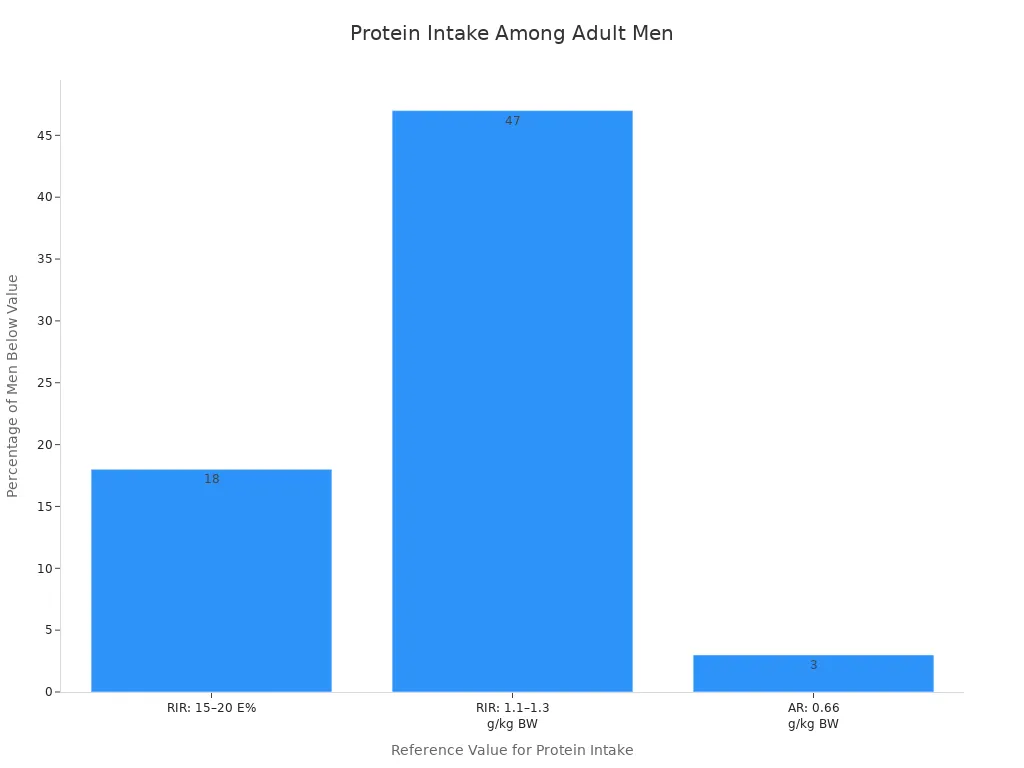
This guide shows how protein fuels your entire day. Getting enough protein is key, because protein matters.
Why Protein Matters for Daily Energy

Protein is more than just a post-workout shake. It is the foundation of your daily energy. An adequate protein intake provides steady power for your body and mind. Understanding these health benefits shows why protein matters for your overall health.
Sustain Energy and Avoid Blood Sugar Crashes
You know the feeling of an afternoon slump after a carb-heavy lunch. Your energy plummets. Protein can prevent this. Your protein intake has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. Eating protein before carbohydrates can even reduce the glucose spike from your meal. This helps you maintain stable energy throughout the day.
Many high-protein foods have a low glycemic index. Foods like lean meats, fish, eggs, and dairy products release energy slowly. This keeps you feeling full and energized without the crash.
A balanced diet with enough protein supports a steady metabolism and consistent energy.
Fuel Your Brain and Sharpen Your Focus
Your brain needs the right fuel to function at its best. Protein provides the essential building blocks for sharp cognitive health. Your body breaks down protein into amino acids. These amino acids are crucial for making neurotransmitters, which are your brain’s chemical messengers.
- L-tryptophan helps create serotonin for mood regulation.
- L-tyrosine is used to produce dopamine for focus and motivation.
Studies show a higher protein intake is linked to better memory. Protein helps maintain neuron integrity and supports brain tissue repair. This contributes to long-term cognitive health and focus.
Enhance Cellular Energy and Oxygen Flow
True energy starts inside your cells. Protein-rich foods deliver essential nutrients that power your cellular metabolism. Iron, a key mineral in foods like red meat, is vital for this process. Iron is a core component of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to every tissue and muscle in your body. Proper oxygen flow is critical for energy production and fighting fatigue.
B vitamins, also found in many protein sources, are cofactors for energy metabolism. They help your body convert the food you eat into ATP, the energy currency of your cells. This process supports everything from muscle function to new cell growth. A diet rich in protein ensures your body has what it needs for optimal performance.
Protein’s Impact on Long-Term Men’s Health
Protein is not just for short-term energy; it is a cornerstone of your long-term health and vitality. A consistent protein intake delivers significant health benefits that compound over time. These benefits support your body’s structure, function, and resilience, showing why protein matters for lifelong well-being.
The Foundation: Protein and Muscle Growth for Function
Your muscle health is vital for everyday function. However, men can start losing muscle mass after age 30. This process, known as sarcopenia, can accelerate with age.
- A typical man can lose 1-2% of his muscle mass per year.
- After age 60, this rate can increase to 3% annually.
Adequate protein and muscle growth are directly linked. Your protein intake provides the essential amino acids needed to stimulate muscle protein synthesis. This process is key for maintaining muscle mass and strength. Consuming enough protein helps you preserve lean muscle, which supports your metabolism and overall physical capability.
Strengthen Your Immune System
A strong immune system protects your overall health. Protein provides the building blocks your body needs to create powerful immune cells. Specific amino acids, including arginine and glutamine, are critical for producing the cells that fight off pathogens. A diet low in protein can weaken your immunity. It impairs your body’s ability to produce antibodies and compromises the function of your immune cells, leaving you more vulnerable to illness.
Support Hormone Balance and Vitality
Hormones regulate everything from your mood to your metabolism. A balanced diet helps maintain optimal health. While protein is essential, moderation is key. Extremely high protein intake can sometimes affect hormone levels, which in turn influences your metabolism. Focusing on a balanced protein intake supports your body’s natural hormone production, contributing to sustained vitality and well-being. This balance is crucial for long-term health.
Build Stronger Bones and Aid Tissue Repair
Your bones need more than just calcium. Collagen, a type of protein, forms the structural framework of your bones. Getting enough protein helps your body produce collagen, which contributes to bone strength and density. Protein is also fundamental for muscle repair and recovery. After exercise or injury, your body uses amino acids from protein to rebuild and strengthen muscle tissue. This process is vital for muscle recovery, growth, and the efficient repair of your body. Proper recovery ensures you are ready for your next challenge.
A Practical Guide to Your Protein Intake

Knowing that protein is important is the first step. The next step is understanding how to apply that knowledge to your daily life. This guide gives you practical tools to optimize your protein intake for better energy and long-term health. You can transform your nutrition and feel the difference.
Why Men Need More Protein for Vitality
You might wonder why men need more protein than women. Several key factors explain this difference. Understanding these reasons helps you tailor your diet for optimal performance and health. In short, men need more protein for vitality.
Your body has unique physiological traits that increase its demand for protein:
- Higher Muscle Mass: You generally have a greater percentage of lean muscle mass, which requires more protein for maintenance and growth.
- Faster Metabolism: Your metabolic rate is often higher, meaning your body burns energy more quickly and needs more fuel.
- Larger Body Size: A larger frame naturally requires more nutrients, including protein, to function correctly.
- Hormonal Profile: Higher levels of testosterone can increase your metabolic rate and support muscle growth, further raising your protein needs.
💡 Simple Guideline for Vitality For general health and energy, aim for 1.0 to 1.2 grams of protein per kilogram of your body weight each day. For a 180-pound (82 kg) man, this equals about 82 to 98 grams of protein daily.
This is higher than the standard recommendation of 0.8 g/kg for sedentary adults. If you are physically active, your needs increase even more. Research suggests active men should consume 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight to support muscle repair and growth. An adequate protein intake is crucial for your overall well-being.
Best Animal-Based Protein Sources
Choosing high-quality sources is key to getting the most from your protein intake. Animal products are complete proteins, meaning they contain all nine essential amino acids your body cannot make on its own. Here are some of the best protein sources from animals.
- Lean Meats (Chicken and Beef)
Chicken breast is a fantastic source of lean protein. It is rich in essential amino acids like leucine, which is vital for muscle repair. Roasting chicken can even increase its available protein content.
Both beef and chicken offer a complete amino acid profile, making them excellent choices for building and maintaining muscle mass.
| Amino Acids | Beef, flank, steak (100g) | Chicken, broiler, breast (100g) |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 66g (132% DV) | 66g (132% DV) |
| Leucine | 4547mg (167% RDI) | 4547mg (167% RDI) |
| Lysine | 5132mg (244% RDI) | 5132mg (244% RDI) |
| Histidine | 1906mg (272% RDI) | 1906mg (272% RDI) |
-
Fatty Fish (Salmon) 🐟 Salmon is one of the best protein sources you can eat. It provides high-quality protein that is easy to digest, supporting muscle health and hormone production. It is also packed with omega-3 fatty acids, which offer powerful benefits for your heart and brain health.
-
Eggs and Dairy 🥚 Eggs are a cost-effective and versatile protein powerhouse. One large egg contains about 6 grams of protein. Greek yogurt and cottage cheese are also excellent dairy sources that provide a slow-releasing protein called casein, perfect for sustained energy.
Top Plant-Based Protein Sources
You do not need to eat meat to build a high protein diet. A well-planned plant-based diet can provide all the protein and essential nutrients you need for energy and health. Many plant foods are excellent protein sources.
Some plants offer complete proteins on their own. These are some of the best protein sources from the plant kingdom:
- Soy products (Tofu, Tempeh, Edamame)
- Quinoa
- Hemp seeds
- Buckwheat
- Spirulina
Other plants, like legumes, are packed with protein and fiber. Adding these to your diet is a great way to boost your nutrition.
| Legume | Protein per Cooked Cup |
|---|---|
| Lentils | 17.9g |
| Black Beans | 15.2g |
| Chickpeas | 14.5g |
Combining for Complete Nutrition Most plant sources are missing one or more essential amino acids. You can solve this by combining different plant foods. This practice ensures you get a complete amino acid profile. Classic pairings like rice and beans or hummus and pita bread create a complete protein. This approach helps you build a balanced diet with a variety of plant-based sources.
Timing Your Protein for Optimal Energy
When you eat protein is just as important as how much you eat. Spreading your protein intake throughout the day helps maintain stable energy levels, control hunger, and maximize muscle health. A balanced diet includes protein at every meal.
Start your day with a protein-rich breakfast. Studies show that a high-protein breakfast increases feelings of fullness and satisfaction for hours. This helps you avoid mid-morning energy crashes and cravings. Both animal and plant-based protein breakfasts are more effective at controlling appetite than a low-protein, high-carb meal.
Distributing your protein evenly across your meals offers another major benefit. Research found that an even distribution boosts 24-hour muscle protein synthesis by about 25% compared to eating most of your protein in one large evening meal. This means your body can more effectively repair and build muscle tissue throughout the day.
🎯 Target Per Meal For optimal muscle health and energy, aim to consume 20-30 grams of high-quality protein with each meal. This simple strategy helps you meet your daily goal and ensures your body has a steady supply of amino acids for growth and repair.
By focusing on these high-quality sources and timing, you can build a diet that fuels your body for peak performance and lasting vitality.
Prioritizing your protein intake is a cornerstone strategy for enhancing your daily energy and long-term health. A consistent protein intake delivers significant health benefits. It supports stable energy, a stronger immune system, better hormone health, and improved physical function. Experts agree that spreading your protein throughout the day is crucial for your health. This is why protein matters.
Start today by incorporating a quality source of protein into every meal to feel your best.
FAQ
Can you eat too much protein?
Yes, an excessive protein intake can strain your kidneys over time. You should stick to the recommended range for your activity level. A balanced diet is key for long-term health. Most men do not need an extreme amount of protein.
Is protein important if I don’t lift weights?
Absolutely. Your body needs protein for daily functions. It helps maintain your existing muscle mass and strength. Adequate protein supports your energy levels and overall health, regardless of your workout routine. You need it to preserve your muscle.
Are protein shakes better than whole foods?
Whole foods are generally better. They offer more nutrients than just protein. You can use protein shakes for convenience, especially after a workout. Shakes should supplement your diet, not replace whole food protein sources.
How does protein help with muscle recovery?
Your muscles need protein for repair and recovery. Exercise creates tiny tears in your muscle fibers. Your body uses amino acids from protein to heal this muscle damage. This recovery process leads to muscle growth and improved strength. These amino acids are essential for muscle recovery.
See Also
Protein and ADHD: A Scientific Guide for Health-Conscious Families
Unlocking Wellness: The Science-Backed Benefits of 5-MTHF Supplements
Methylated Vitamins: Key to Optimal Absorption and Enhanced Wellness
Understanding ADHD and Protein: A Beginner’s Essential Guide
Protein and ADHD: A Beginner’s Guide to Their Vital Connection

 Both beef and chicken offer a complete amino acid profile, making them excellent choices for building and maintaining muscle mass.
Both beef and chicken offer a complete amino acid profile, making them excellent choices for building and maintaining muscle mass.