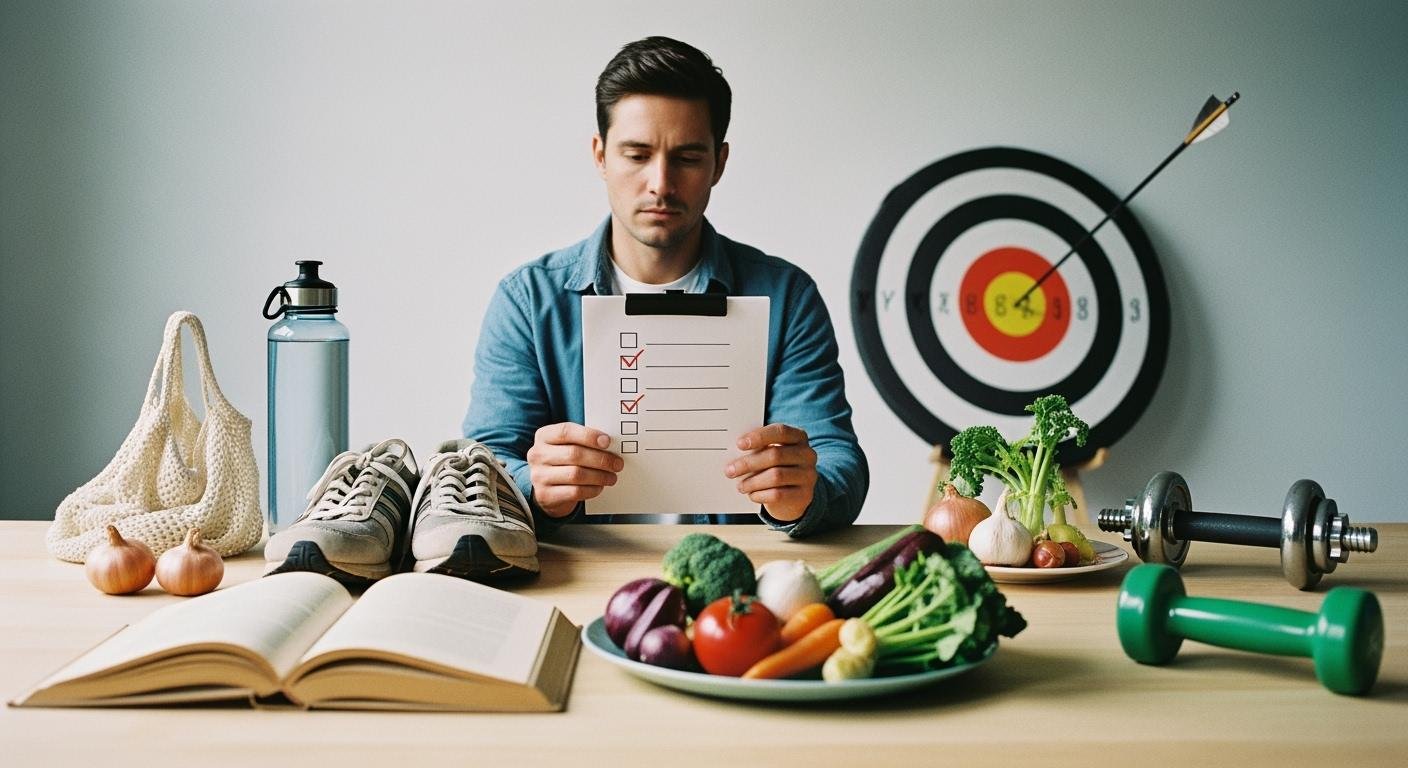
You might wonder why men fail at wellness goals, even when they try hard. Mental barriers and social expectations make things tough. Many men feel embarrassed or fear being seen as weak, which stops them from asking for help. Emotional suppression and traditional masculinity norms create extra hurdles. Men who aim to lose 5-10% of their weight succeed 28% of the time, while women succeed 20% of the time. Think about your own challenges and stay open to new habits.
- Emotional suppression holds many men back.
- Fear of weakness stops men from seeking help.
- Men succeed in weight loss more often than women but still face big barriers.
Why Men Fail at Wellness Goals
Common Barriers Men Face
You probably notice that men fail at wellness goals for reasons that go beyond simple effort. Many barriers stand in your way. You might feel too tired or believe work gives you enough exercise. Sometimes, you run out of time or feel intimidated by physical activity. Traditional norms push you to ignore your own health and focus on professional responsibilities. You may neglect self-care because guilt creeps in. Social pressure makes you resist seeking support, so you avoid community-based mental health services. When you try to access treatment, you might worry about appearing weak. Over-reliance on motivation leads to setbacks, and having too many goals can cause disengagement from services. Information overload creates anxiety and guilt, making you question your self-worth. Social media targets your insecurities, and you compare yourself to fitness influencers. These barriers often lead to disengagement from health routines and treatment.
- Vague goals make progress hard to track.
- Guilt about self-care leads to neglect.
- Lack of support results in self-sabotage.
- Too many goals overwhelm you.
- Information overload causes disengagement.
The Role of Mental Blocks
Mental blocks play a huge part in why men fail at wellness. You might struggle to express feelings or access mental health support. Toxic masculinity creates restrictive emotionality, making it tough to seek treatment. You avoid vulnerability and disengagement from services. Motivation to approach success boosts well-being, but motivation to avoid failure reduces it. High self-control helps you monitor these mental barriers. Many men delay access to mental health services, sometimes for years. You may question yourself instead of the unrealistic standards set by society. This cycle leads to disengagement from health routines and treatment. When you finally access services, you redefine your identity and see help-seeking as responsible. Engagement with mental health services improves your well-being and helps you overcome barriers.
Tip: Recognizing mental barriers and emotional blocks is the first step toward better health and treatment. You can access services and build lasting routines.
| Emotional Barrier Type | Influence on Motivation | Self-Control Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Motivation to Approach Success | Enhances well-being | Stronger for high self-control |
| Motivation to Avoid Failure | Reduces well-being | Monitored better by high self-control |
Set Clear, Specific Goals

Vague Goals vs. Actionable Steps
You might set a goal like “get healthier,” but that leaves you lost. Vague goals often lead to failure because you lack a clear plan. Only 8% to 10% of people reach their New Year resolutions. Most miss out because they skip structured planning and measurable benchmarks. You need specific, measurable objectives to boost your success rate. Studies show that men who set clear goals achieve more than those who stick with vague ideas. Behavioral science proves that measurable steps help you stay on track and avoid losing direction.
Try using the SMART goal method. This means your goals are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. You can focus on core pillars like physical fitness, mental resilience, and lifestyle balance. Start with small steps. Join a walking challenge or a running club. Build a healthy work environment and promote open communication. Mental health resources and wellness champions can guide you.
Tip: Break your big goal into smaller, actionable steps. This makes progress easier to track and keeps you motivated.
Building Confidence in Success
You need confidence to succeed. Mental toughness and coping strategies help you stick with wellness programs. The Building Healthy Men Project found that self-confidence grows when you join all-male support groups and use sports to talk about mental health. Elite rugby players show that mental strength links to better outcomes.
| Intervention Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Cognitive Restructuring | Challenge negative mental patterns and picture a successful future. |
| Optimism Interventions | Build hope and agency to face mental obstacles and improve well-being. |
| Meaning-oriented Activities | Find meaning in daily tasks and set realistic mental goals. |
| Positive Affirmations | Use statements to boost mental self-belief and motivation. |
You can use mental strategies like positive affirmations and optimism exercises. These help you believe in your ability to reach your goals. When you build mental confidence, you engage more and see better results.
Why Self-Care Is Hard for Men
Male Neglect of Self-Care
You probably notice that self-care hard for men. Many barriers make it tough for you to focus on your own health. Society expects you to provide for your family, raise children with strict discipline, and show strength. You often limit emotional expression to anger and avoid vulnerability. You might feel pressure to stay physically fit and engage in masculine hobbies. Seeking medical help or mental health services feels like weakness. You may neglect self-care practices because you think you should take charge in every situation. This leads to self-neglect and poor health.
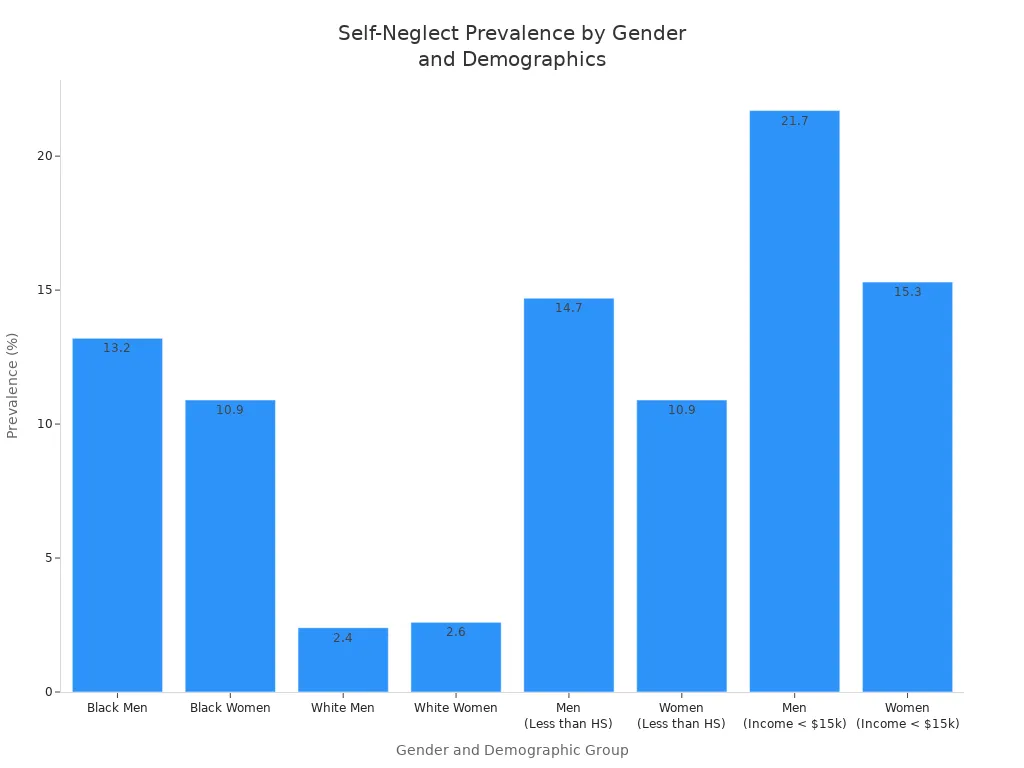
Here’s a quick look at self-neglect rates:
| Gender | Prevalence of Self-Neglect (%) | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Black Men | 13.2 | 11.2–15.3 |
| Black Women | 10.9 | 9.5–12.3 |
| White Men | 2.4 | 1.2–3.6 |
| White Women | 2.6 | 1.7–3.6 |
| Men (Less than HS) | 14.7 | N/A |
| Women (Less than HS) | 10.9 | N/A |
| Men (Income < $15,000) | 21.7 | N/A |
| Women (Income < $15,000) | 15.3 | N/A |
You may experience mental health symptoms alone. Stigma and barriers stop you from talking about mental health or seeking treatment. Many men use unhealthy coping methods like alcohol or drugs, which can worsen mental health.
Overcoming Guilt and Stigma
Guilt makes you avoid self-care. You might see self-care as lazy or weak. Stigma and mental barriers push you to ignore your needs. This guilt leads to self-neglect and poor health. You can break these barriers by trying a few strategies:
- Programs like Decoding Masculinity & Mental Health help you manage emotions and expectations.
- Calm Health gives you personalized mental health services and treatment plans.
- Employers can support you by checking mental health, encouraging open talks, and building a culture of care.
Tip: You deserve care and treatment. Prioritize self-care without guilt. Small steps help you build mental health and well-being.
Build Support and Accountability

Breaking Isolation Barriers
You might feel alone when you try to improve your health. Isolation creates barriers that block your engagement with self-care and mental health routines. Research shows that social isolation affects about a third of people in industrialized countries. It can lead to depression, anxiety, and even heart problems. When you stay isolated, you risk disengagement from health services and treatment. Neuroendocrine pathways triggered by loneliness can cause long-term mental health issues, including cognitive decline and inflammation. Observational studies link isolation to higher mortality rates. You need strategies to access community and support networks to break these barriers.
- Supportive connections matter more than the number of relationships.
- Community-based supports combined with clinical expertise help men maintain wellness routines longer.
- Peer accountability networks boost engagement and reduce disengagement.
You can access services like psycho-educational health programs, leisure activities, and choir groups. These strategies improve psychological well-being and decrease loneliness, though some challenges like participant drop-out exist.
| Intervention Type | Target Outcomes | Results | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Psycho-educational health programs | Mastery, health behaviour, depression, social isolation, loneliness | Improved psychological wellbeing; poor ratings on loneliness and social isolation | Participant drop-out rates |
| Leisure/skill development activities | Psychosocial, cognitive, physical wellbeing | Increased social connectedness; decreased loneliness | Significant loss to follow-up |
| Choir intervention | Loneliness, interest in life, positive affect | Decreased loneliness; increased interest in life | No significant differences in primary outcomes |
Finding Your Wellness Tribe
You need a community to stay motivated. Peer groups offer emotional and practical support, encourage healthy behaviors, and create friendly competition. Shared experiences build identity and boost engagement with self-care and mental health routines. You prefer groups of similar individuals, which increases your sense of belonging. The FFIT study highlights banter and comradery as strong motivators. Peer support helps you access services, maintain treatment, and avoid disengagement. Try joining a wellness tribe, whether it’s a sports team, walking club, or online community. These strategies help you access care, build support, and stay engaged with health routines.
Tip: Reach out to your community and peer groups. You can access support, care, and treatment. Engagement with services and peer support leads to lasting wellness.
Focus on Consistency, Not Motivation
Why Motivation Fails
You probably feel pumped up when you start a new health routine. Motivation gives you a quick boost, but it fades fast. You might push yourself hard for a few days, then lose steam and slip back into old habits. Relying on motivation alone leads to inconsistency and disengagement. Intense efforts can cause burnout and make you avoid self-care. You need mental strategies that help you stick with routines, even when motivation drops. Consistency leads to long-term health success. Small daily habits become part of your lifestyle and support lasting results. Sustainable fitness routines work better than extreme plans that are hard to maintain. You can access mental health services and build engagement with community support. Peer support helps you stay on track and avoid disengagement from health routines.
Note: Consistency beats motivation every time. You build mental strength and access care by showing up, even when you don’t feel motivated.
Creating Lasting Habits
You want lasting health habits, not quick fixes. Behavioral science shows that you can use strategies to make routines stick. Try habit stacking. Link a new self-care habit to something you already do, like brushing your teeth. Reward systems help you feel good about progress and boost engagement. Visual progress tracking lets you see your wins and builds momentum. Focus on consistency over perfection. You don’t need to be perfect, just keep showing up. Community engagement and peer support make routines easier. Access services that offer mental health care and support. You can build engagement with self-care and avoid disengagement from health routines. Community strategies help you access care and stay connected. Mental health routines become easier with support from community services.
- Habit stacking
- Reward systems
- Visual progress tracking
- Consistency over perfection
| Strategy | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Habit stacking | Easier self-care routines |
| Reward systems | Boosts engagement |
| Visual tracking | Builds momentum |
| Community support | Reduces disengagement |
Simplify and Prioritize Goals
Avoiding Overwhelm
You might feel overwhelmed when you try to improve your health. Too many goals and too much information can make you want to give up. Many men face pressure from work, family, and society. These pressures can hurt your mental health and lower your engagement with wellness routines. Take a look at some common causes of overwhelm:
| Cause of Overwhelm | Impact on Mental Health |
|---|---|
| Societal Expectations | Contributes to anxiety, depression, and burnout |
| Job Stress | Heightens feelings of inadequacy and self-worth |
| Mental Health Challenges | Leads to a cycle of pushing beyond limits |
| Traditional Masculinity Norms | Prevents seeking help and addressing issues |
| High-Pressure Work | Increases risk of mental health struggles |
You do not have to tackle everything at once. When you focus on too many things, your engagement drops. You might stop reaching out to your community or using peer support. This can make you feel alone and less likely to keep up with your health goals.
Choosing What Matters Most
You can boost your engagement by picking a few high-impact habits. Experts suggest some simple strategies:
- Set meaningful wellness goals that match your values.
- Make small, steady changes to your daily habits.
- Focus on nutrition and regular exercise for better health.
- Address mental health challenges with stress management.
- Use peer and community support to stay on track.
Try to connect with your community and build a network of support. Peer groups can help you stay motivated and share tips. When you focus on what matters most, you increase your engagement and make real progress. Remember, your health journey is easier when you use support from your community and peers.
Tip: Choose one or two goals that matter most to you. Build engagement with your community and peer support. This will help you reach your health goals and feel better every day.
You see men fail at wellness when they ignore mental habits. Start with one habit. Build momentum. Focus on mental health. Use mental strategies. Join mental health groups. Track mental progress. Talk about mental health. Share mental wins. Overcome mental barriers. Take charge of mental health.
You can change how men fail at wellness. Mental health matters every day.
FAQ
What is the biggest reason men fail at wellness goals?
You often set vague goals. You may lack support. Social pressure and mental barriers make it harder for you to stay consistent.
How can you start building better wellness habits?
Try small steps. Join a group. Track your progress. Focus on one habit at a time. You will see results faster.
Why does mental health matter in your wellness journey?
Mental health shapes your motivation and confidence. You need to address it to build lasting habits and reach your goals.
See Also
Exploring Methylated Vitamins: Unlocking Wellness Through Absorption
Discovering 5-MTHF: Science-Driven Benefits for Wellness
Understanding ADHD: An Introductory Guide to Protein’s Role