Your body reacts to daily stress by changing how much cortisol it makes. This hormone helps you stay alert and handle challenges. You might notice your energy shifts or moods change during the day. Recent studies show that while your total daily cortisol stays pretty steady, short-term changes are normal.
| Cortisol Index | Stability Over Time | Variance Attribution |
|---|---|---|
| Total Daily Output | Most stable | 50% day-to-day fluctuations |
| Diurnal Slope | Moderately stable | Majority from short-term changes |
| Cortisol Awakening Response (CAR) | Least stable | Primarily state-like properties |
When you learn about your cortisol levels, you can find ways to manage stress and take care of your health.
What Is Cortisol?
Cortisol is a hormone your body makes every day. You might hear people call it the “stress hormone,” but it does much more than help you deal with tough moments. Your adrenal glands produce cortisol, and it travels through your blood to help your body work smoothly. You need cortisol for energy, alertness, and keeping your body balanced.
Cortisol’s Role in Stress Response
When you face stress, your body releases more cortisol. This helps you react quickly and stay focused. Cortisol gives your brain a boost by sending extra glucose into your bloodstream. You feel more alert and ready to handle challenges. Your body also uses cortisol to break down proteins, fats, and sugars, so you have enough fuel for action.
Here are some ways cortisol helps you during stress:
- Raises your blood sugar for quick energy.
- Supports your metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
- Influences your sleep-wake rhythm, so you feel awake in the morning.
- Controls blood pressure and helps your immune system respond.
- Reduces inflammation when your body needs to heal.
Cortisol also interacts with other hormones. High cortisol can lower estrogen and testosterone, which may cause hormonal imbalances. It can also affect your thyroid and insulin, making it harder for your body to use sugar.
Why Healthy Cortisol Levels Matter
You need healthy cortisol levels to feel your best. Too much or too little cortisol can cause problems. If your cortisol stays high for a long time, you might feel tired, gain weight, or notice mood swings. Your blood pressure can go up, and your immune system may not work as well. Some people with high cortisol develop conditions like Cushing’s syndrome, which causes muscle weakness and fatigue.
Doctors use healthy ranges to check cortisol levels. Here’s a quick look at what’s normal:
| Age Group | Morning (mcg/dL) | Afternoon (mcg/dL) | Evening (mcg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Children (0–12) | 3–21 | N/A | N/A |
| Adolescents (13–18) | 5–23 | 3–13 | 1–8 |
| Adults (19–60) | 6–23 | 2–14 | 1–8 |
| Seniors (60+) | 4–18 | 1–10 | 0–6 |
Tip: If you notice changes in your energy, mood, or sleep, it might be a sign your cortisol is out of balance. Paying attention to these signals can help you stay healthy.
Stress and Cortisol Release
How Stress Triggers Cortisol
When you feel stress, your body jumps into action. Your brain senses a threat or challenge, and it sends out signals to get you ready. This is where the stress hormone, cortisol, comes in. Your hypothalamus, a small part of your brain, starts the process by releasing a chemical called CRH. This chemical tells your pituitary gland to send out ACTH. ACTH travels through your blood to your adrenal glands, which sit on top of your kidneys. Your adrenal glands then release cortisol into your bloodstream.
Here’s how your body’s response works, step by step:
- Your brain detects stress and releases CRH.
- CRH tells your pituitary gland to release ACTH.
- ACTH signals your adrenal glands to release cortisol.
Cortisol helps you handle stress by giving you quick energy. It raises your blood sugar, so your muscles and brain have the fuel they need. It also helps your heart pump faster and your lungs take in more oxygen. This is called the “fight-or-flight” response. You might notice your heart racing or your hands getting sweaty. These are signs of stress and your body’s way of getting ready to act.
Your body also uses cortisol to control inflammation and keep your immune system in check. When you face chronic stress, your body keeps making cortisol. Over time, this can lead to problems with your health.
Glucose plays a big role in this process. When you eat sugar or carbs, your body has more glucose available. Studies show that having more glucose can make your cortisol response to stress even stronger. This means your body reacts more quickly and with higher levels of the stress hormone.
Not all stress is the same. Physical stress, like running or getting hurt, can cause a quick spike in cortisol. Emotional stress, like worrying about a test, also triggers cortisol. Environmental stress, such as living in a noisy or unsafe neighborhood, can change your cortisol pattern over time. People who live with chronic stress from their environment may have lower overall cortisol levels during the day. This can affect your health in different ways.
Cortisol does not stay high forever. After a stressful event, your cortisol level rises and then slowly drops back to normal. Here’s a quick look at how cortisol changes after stress:
| Time After Stressor | Cortisol Level Status |
|---|---|
| 0 minutes | Baseline |
| 20-25 minutes | Peak |
| 60-70 minutes | Return to baseline |
Your body is always working to keep your cortisol balanced. This helps you recover after stress and get back to feeling normal.
Symptoms of Elevated Cortisol
When your body makes too much cortisol, you might start to notice changes. These changes are the consequences of elevated cortisol and can affect both your body and your mind. Some symptoms show up quickly, while others take time to develop, especially if you deal with chronic stress.
Physical symptoms of high cortisol include:
- Weight gain, especially around your waist
- Acne or skin problems
- High blood pressure
- Headaches
- Stomach issues like pain, constipation, or diarrhea
- Feeling thirsty more often
- Trouble sleeping or insomnia
You might also notice emotional or mental changes, such as:
- Feeling anxious or nervous
- Brain fog or trouble focusing
- Feeling sad or depressed
- Tiredness that doesn’t go away
- Getting irritated easily
These are some of the most common consequences of elevated cortisol. If you notice several of these symptoms, your body might be telling you that your stress hormone levels are too high. Chronic stress can make these symptoms worse and harder to manage.
Many people, especially middle-aged women, report higher stress and more health problems linked to elevated cortisol. Even though not everyone will have all these symptoms, it’s important to pay attention to how you feel. Managing stress response early can help you avoid long-term health issues.
If you spot these signs of stress in your daily life, you can take steps to lower your cortisol and protect your health. Simple changes, like getting enough sleep, eating well, and finding ways to relax, can make a big difference.
Health Effects of High Cortisol

Short-Term Impacts
When your cortisol levels rise for a short time, you might notice changes in your mood and thinking. This hormone helps you react to stress, but too much can make you feel anxious or sad. You may find it hard to focus or remember things. Sometimes, you feel tired even after a good night’s sleep. Your body uses hormones to keep you alert, but high cortisol can throw off your balance.
Here’s what you might experience when cortisol spikes:
- Trouble remembering things or paying attention
- Feeling nervous or worried
- Mood swings, like feeling sad or angry
- Brain fog that makes it hard to think clearly
Older adults often notice memory problems when cortisol stays high. Your hormones work together, so when one hormone changes, others can shift too. This can affect your energy and how you handle stress. If your cortisol stays at a moderate level, you may feel sharp and focused. Both low and high levels can make thinking harder.
If you notice these changes, your body might be telling you to slow down and take care of your health.
Long-Term Risks
If your cortisol stays high for a long time, your health can suffer. This hormone affects many parts of your body. You may gain weight, especially around your belly. Your blood sugar can rise, which increases your risk for diabetes. High cortisol can change how your hormones work, leading to problems with your heart and bones.
Here are some risks you face with long-term high cortisol:
- Obesity and high blood sugar
- High blood pressure and heart disease
- Weak muscles and bones
- More infections because your immune system slows down
- Mood disorders and trouble concentrating
- Skin changes, like thinning or acne
- Problems with your menstrual cycle or sexual health
Doctors see that cortisol can change how your body handles glucose and fat. This hormone can disrupt your daily rhythm and make your body less sensitive to insulin. You may notice your physical health getting worse over time. Studies show that half of deaths from heart disease linked to metabolism could be prevented if you manage these risk factors.
| Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
| Cortisol’s Role | Cortisol can raise your risk for heart disease by changing how your body handles fat, sugar, and blood pressure. |
| Metabolic Syndrome | These changes can lead to clogged arteries and heart attacks. |
| Preventable Deaths | Many deaths from heart disease could be avoided by keeping your hormones balanced and your cortisol in check. |
Keeping your hormones balanced helps protect your health. If you manage your stress and keep your cortisol steady, you lower your risk for serious health problems.
How to Lower Cortisol Levels
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Stress Hormones
You can take simple steps every day to reduce stress hormones and support your mental health. When you make small changes, you help your body keep cortisol in check. Regular physical activity is one of the best ways to lower cortisol levels. If you move your body, you train it to handle stress better. Exercise gives you a quick boost in cortisol, but over time, it helps your body recover faster and keeps your hormones balanced. You might notice better sleep and more energy when you stay active.
Social support also plays a big role. When you join group activities or spend time with friends, you feel connected. This sense of belonging helps reduce stress hormones and improves your mental health. Team sports or group workouts can make you feel happier and less anxious.
Here are some lifestyle changes you can try:
- Get moving with regular physical activity, like walking, biking, or playing sports.
- Prioritize rest and get enough sleep every night.
- Practice gratitude by thinking about good things in your life.
- Try meditation or deep breathing to calm your mind.
- Eat a healthy diet with lots of whole foods.
If you use stress management techniques such as mindfulness or exercise, you can see real changes. Studies show that people who practice these techniques have lower hair cortisol levels and less anxiety. Most people in these groups report feeling less stressed, while those who skip these habits often see their stress hormones go up.
Tip: You don’t need to make big changes all at once. Start with one new habit and build from there. Even small steps can help you manage stress and support your mental health.
Diet for Healthy Cortisol Levels
What you eat can change how your body handles stress hormones. If you want to maintain healthy cortisol levels, focus on foods that help your body stay balanced. Diets high in fruits and vegetables, like the Mediterranean diet, may decrease cortisol and support mental health. Whole food diets also help reduce stress reactions and keep your hormones steady.
Check out this table to see how different foods and nutrients affect cortisol:
| Dietary Pattern/Nutrient | Effect on Cortisol Levels |
|---|---|
| Potassium supplementation | Possible elevation of cortisol concentration |
| Multi-strain probiotic supplements | Improvement in free urinary cortisol |
| Ketogenic diet (KD) | May decrease cortisol levels |
| Evening high-glycemic meals | Raises cortisol due to neuroendocrine mechanisms |
| Mediterranean diet | May decrease urinary cortisol levels |
| High intake of saturated fats | Alters daytime cortisol levels |
| Low intake of fruits/vegetables | Associated with high cortisol concentration |
| Whole food diets (DGA) | Potential to mitigate stress reactions and cortisol levels |
| Fermented foods | Associated with reduced social anxiety |
| Dietary sugar/carbohydrate | Dampens stress-induced elevation in cortisol |
If you eat more saturated fats and fewer fruits and vegetables, you might see higher cortisol. On the other hand, whole food diets and fermented foods can help you feel calmer and support mental health. Probiotics may also improve your body’s response to stress.
Caffeine and sugar can change how your body releases cortisol. If you drink coffee and don’t do it often, you might notice a spike in cortisol. Regular coffee drinkers get used to it, so their bodies don’t react as strongly. Sugar can actually dampen cortisol after stress, which is why comfort foods sometimes help you feel better. Still, it’s best to eat sugar in moderation and focus on balanced meals.
Note: Eating a variety of whole foods and limiting processed snacks can help you maintain healthy cortisol levels and support your mental health.
Sleep and Relaxation Techniques
Getting adequate sleep is one of the most important factors that influence cortisol levels. If you get enough sleep, your body can recover and keep stress hormones balanced. Poor sleep can lead to higher cortisol and make it harder to manage stress. People who sleep less often have a flatter cortisol awakening response and shorter sleep times. This can make you feel tired and affect your mental health.
Here’s a table showing how sleep affects cortisol rhythms:
| Evidence Type | Findings |
|---|---|
| Bidirectional Interaction | Poor sleep can lead to altered cortisol patterns, while elevated cortisol can disrupt sleep. |
| Cortisol Awakening Response | Low sleep quality leads to a flatter CAR and shorter sleep time. |
| HPA Axis Impact | High cortisol increases wakefulness and reduces slow-wave sleep. |
If you want to maintain healthy cortisol levels, aim for 7 to 9 hours of adequate sleep each night. Try to keep a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine. This helps your body reset and lowers stress hormones.
Relaxation techniques can also help you reduce stress hormones and support mental health. Mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing are proven ways to lower cortisol. A recent meta-analysis found that mindfulness and meditation, as well as relaxation techniques like progressive muscle relaxation, are among the most effective methods for lowering cortisol levels.
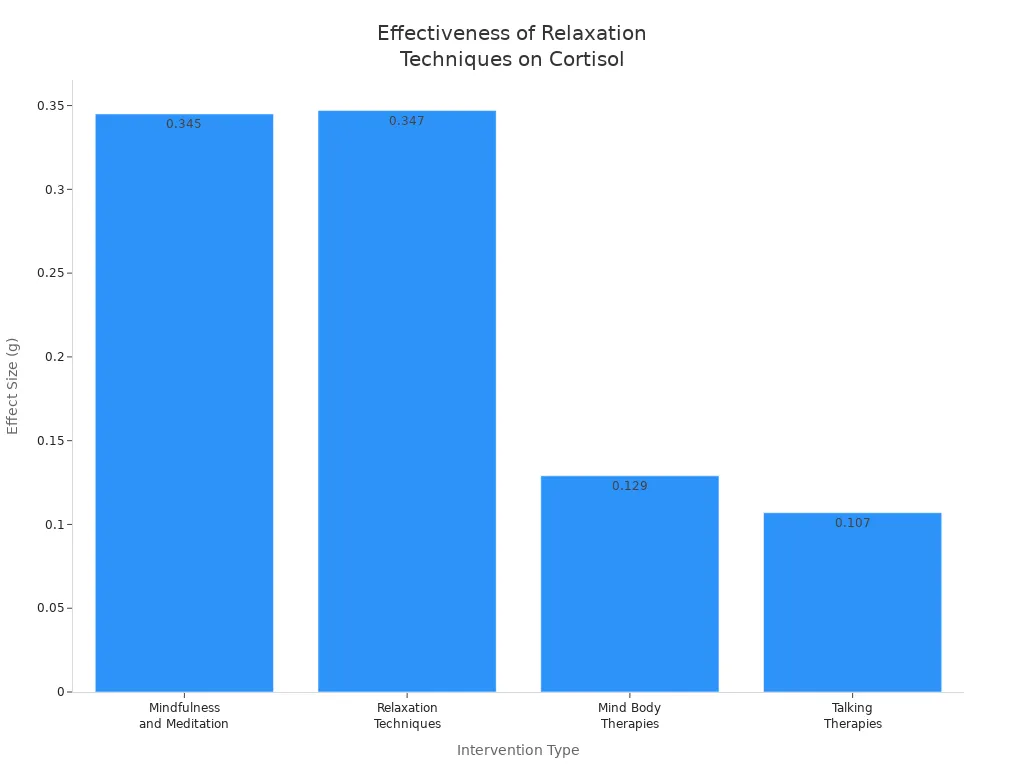
You can try these relaxation techniques:
- Mindfulness meditation
- Guided breathing exercises
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Gentle yoga or stretching
If you use these stress management techniques, you can see a real difference in your mental health and how your body handles stress. Most people feel calmer, sleep better, and notice fewer symptoms of anxiety.
Callout: Make relaxation part of your daily routine. Even five minutes of deep breathing or meditation can help you reduce stress hormones and support your mental health.
By focusing on regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, and practicing relaxation techniques, you can manage stress and support healthy cortisol levels. These habits help you feel better, think clearer, and protect your mental health. If you keep up with these changes, you’ll find it easier to maintain healthy cortisol levels and enjoy a happier, healthier life.
You can take charge of your stress and support healthy cortisol levels with simple habits. Try these steps:
- Eat a balanced diet with fruits and veggies.
- Get enough sleep each night.
- Move your body every day.
- Practice deep breathing or meditation.
- Enjoy creative hobbies.
Remember, everyone feels stress sometimes. Small changes can make a big difference for your mood, energy, and health. If you need extra help, reach out to a trusted resource or talk to someone you trust. You’ve got this! 😊
FAQ
What is the best way to check my cortisol levels?
You can ask your doctor for a blood, saliva, or urine test. These tests show your cortisol levels at different times of day. Home kits are available, but you should talk to a healthcare provider for accurate results.
Can stress make my cortisol stay high all the time?
Chronic stress can keep your cortisol elevated. You might feel tired, anxious, or have trouble sleeping. If you notice these signs, try relaxation techniques or talk to someone you trust.
Do kids and teens have different cortisol patterns than adults?
Yes! Kids and teens usually have higher morning cortisol. Their levels change as they grow. You might notice mood swings or energy shifts during puberty. Healthy sleep and good nutrition help keep their cortisol balanced.
Will exercise always lower my cortisol?
Exercise helps your body manage stress. Short workouts can raise cortisol for a little while, but regular activity lowers it over time. You feel better, sleep deeper, and handle stress more easily.
See Also
Exploring How Protein Affects ADHD: A Family Guide
Finding the Optimal Time for Methylfolate Supplement Intake
Understanding the Link Between Protein Intake and ADHD
The Connection Between Protein Consumption and ADHD Explained
Exploring 5-MTHF Benefits: A Scientific Approach to Wellness