Antioxidants are your body’s defense system. They protect your cells from daily damage. This damage comes from unstable molecules called free radicals.
Think of antioxidants as a natural “off-switch.” They stop harmful free radicals from causing problems. 💡
This protective function is very important for your health. It helps to reduce the risk of chronic diseases. These diseases include conditions like heart disease.
Understanding Antioxidants: How They Work
To appreciate what antioxidants do, we first need to look at the problem they solve. The core of understanding antioxidants lies in their relationship with unstable molecules called free radicals.
Neutralizing Free Radicals
Your body is constantly exposed to free radicals. These are unstable molecules missing an electron. This instability makes them highly reactive. They search the body to steal an electron from a healthy, stable molecule. This process is called oxidation.
When a free radical steals an electron, it damages the healthy molecule. That molecule then becomes a new free radical. This starts a harmful chain reaction, causing free radical damage inside your body. This process of oxidation can harm important parts of your cells, like proteins, lipids (fats), and even your DNA.
Where do these molecules come from?
- Internal Processes: Your body naturally produces them when it converts food into energy.
- External Factors: You are also exposed to them from the environment. Sources include air pollution, cigarette smoke, industrial chemicals, and even sunlight.
This is where antioxidants step in to fight free radicals. Antioxidants are stable molecules with electrons to spare. They can safely donate an electron to neutralize free radicals. This generous act stops the damaging chain reaction of oxidation before it can prevent cell damage.
Think of it this way: An antioxidant gives a free radical what it wants (an electron) without becoming unstable itself. This simple donation acts as an “off-switch” for cellular damage. 🛡️
Reducing Oxidative Stress
Your body has its own defense system, including antioxidant enzymes, to handle a normal level of free radicals. However, problems arise when this system is overwhelmed.
Oxidative stress is the imbalance that occurs when the number of free radicals is too high for your body’s antioxidants to manage. This imbalance can happen from prolonged exposure to pollutants or a poor diet lacking foods with antioxidant properties.
When oxidative stress becomes chronic, the constant oxidation can lead to serious health issues. Scientists have linked long-term oxidative stress to many conditions, including:
- Heart disease
- Neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s
- Certain types of cancer
- Chronic inflammation and joint problems
Doctors can even measure the effects of oxidation in the body by looking for biomarkers of damage. Maintaining a diet rich in antioxidants helps your body manage this balance, reducing oxidative stress and protecting your long-term health.
Health Benefits of Antioxidants
By neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, antioxidants provide significant health benefits. Their work helps protect your body from cellular damage. This protection plays a key role in preventing chronic diseases and promoting overall wellness.
Supports Heart Health
Antioxidants are powerful allies for your cardiovascular system. They help maintain good heart health in several ways. Oxidative stress can damage blood vessels and contribute to the buildup of plaque in arteries. This increases the risk of heart disease.
Studies show a clear link between a diet high in antioxidants and better heart outcomes. Research using a Dietary Antioxidant Index found that people with higher antioxidant intake had a reduced risk of heart attacks. This protective effect of antioxidants helps lower the risk for cardiovascular problems.
Specific compounds like polyphenols and flavonoids are especially beneficial.
- They scavenge harmful free radicals in the bloodstream.
- They can block enzymes that produce these damaging molecules.
- Some, like quercetin, can bind to metal ions, preventing them from creating more free radicals.
Clinical trials also support these benefits. Diets rich in antioxidants have been shown to improve cholesterol levels. For example, one study found that patients on an antioxidant-rich diet had lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol. Other studies show that certain foods can help manage blood pressure.
Did You Know? 💡 Many plant-based foods have been studied for their positive effects on heart health. The table below shows a few examples from clinical trials.
| Plant Source | Study Outcome |
|---|---|
| Orange Juice | Improved LDL cholesterol and blood glucose |
| Haskap Berry | Lowered blood pressure and improved memory |
| Pomegranate | Lowered systolic blood pressure |
| Beetroot Juice | Lowered blood pressure in various groups |
| Oat Noodles | Reduced cholesterol ratios and blood pressure |
Combating Free Radical Damage and Disease Risk
The chain reaction of free radical damage is a major factor in the development of many diseases. When DNA, proteins, or lipids are damaged by oxidation, it can lead to serious health problems. Chronic oxidative stress is also linked to chronic inflammation, which is a root cause of many long-term illnesses.
This is where antioxidants make a big difference. They stop this damage before it can cause lasting harm. For instance, research shows that high levels of vitamin C can prevent DNA mutations caused by oxidative stress. By protecting your DNA, antioxidants help lower the risk of changes that could lead to diseases like cancer.
Emerging research even suggests a link between cancer and heart damage caused by free radicals. Studies in animal models found that tumors increased the production of free radicals, which then harmed the heart. Adding antioxidants to the diet reversed this damage. This highlights how antioxidants can help manage the widespread effects of serious diseases. A diet rich in these compounds is associated with a decreased risk of:
- Cardiovascular disease and related mortality
- Certain types of cancer
- Mood disorders
Eating a variety of antioxidant-rich foods helps your body fight constant free radical damage. This simple dietary habit can lower your overall risk of health issues.
Boosts Your Immune System
Your immune system is a complex network of cells that defends your body against infection. This system requires a lot of energy and is vulnerable to oxidative stress. Antioxidants play a vital role in supporting your immune cells and helping them function properly.
They help in two main ways:
- Reducing Inflammation: Free radicals can trigger inflammation. Antioxidants help control this process, which is important for recovering from infections.
- Protecting Immune Cells: Immune cells themselves use free radicals to destroy pathogens. Antioxidants protect the immune cells from being damaged in the process.
Specific antioxidants provide unique benefits to the immune system. They help your body respond to infections and maintain a strong defense.
| Antioxidant | Role in Immune Support |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Stimulates the production and function of white blood cells. |
| Vitamin E | Improves T-cell function and the activity of natural killer cells. |
| Zinc | Helps immune cells like macrophages and neutrophils function correctly. |
| Selenium | Needed to make glutathione, the body’s “master antioxidant.” |
| Polyphenols | Have anti-inflammatory properties and support mucosal immunity. |
Promotes Healthy Aging
Aging is a natural process, but some signs are accelerated by oxidative stress. This includes visible signs like wrinkles and internal issues like cognitive decline. Antioxidants can help slow down this process and promote healthier aging.
On the outside, free radicals break down collagen and elastin. These are the proteins that keep your skin firm and smooth. This damage leads to wrinkles and sagging. Antioxidants protect your skin by:
- Neutralizing the free radicals that attack collagen.
- Helping your body produce new collagen. Vitamin C is an essential part of this process.
On the inside, your brain is also vulnerable to damage. Oxidative stress is linked to age-related diseases and cognitive decline. Antioxidants help protect neurons from this damage. Many studies suggest that a diet high in antioxidants can support cognitive function as you get older. Research has linked higher intakes of vitamins C and E with better memory and slower cognitive decline. While more research is needed, a diet full of colorful fruits and vegetables appears to be a great way to protect your brain.
Best Food Sources of Antioxidants

Getting enough antioxidants is key to protecting your health. The best way to do this is through the food you eat. Your diet can provide a powerful defense against free radical damage.
Focus on Whole Foods, Not Supplements
You might see supplements promising high doses of antioxidants. However, whole foods are a better and safer source of antioxidants. Foods contain a complex mix of nutrients, fiber, and compounds that work together. This teamwork, called synergy, makes the antioxidants in food more effective. Supplements often lack this powerful combination.
High-dose supplements can also carry risks.
- They can interfere with how your body works.
- Some studies show that high levels of beta-carotene supplements may increase lung cancer risk in smokers.
- Too many supplements can even cause an imbalance of nutrients in your body.
Whole foods are naturally balanced. The fiber in fruits and vegetables helps your body absorb nutrients like vitamins C and E slowly and effectively. This makes them easier for your body to use.
Eat a Variety of Colorful Plants
A simple way to add antioxidants to your diet is to “eat the rainbow.” The different colors in fruits and vegetables come from different antioxidant compounds. Eating a variety of colors ensures you get a wide range of health benefits. You should try to get a mix of these antioxidants every day.
Each color group offers unique protection:
| Color Group | Key Antioxidants | Found In |
|---|---|---|
| Red/Pink | Lycopene, Anthocyanins | Tomatoes, Strawberries, Watermelon |
| Orange/Yellow | Carotenoids | Carrots, Sweet Potatoes, Oranges |
| Green | Lutein, Chlorophyll | Spinach, Kale, Broccoli |
| Blue/Purple | Anthocyanins | Blueberries, Eggplant, Blackberries |
Top Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Some foods are packed with more protective compounds than others. A diet high in antioxidants often includes plenty of berries, beans, and leafy greens. Dark chocolate is another one of the good sources of specific antioxidants.
Scientists can measure the antioxidant power of foods using an ORAC score (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity). Foods with a higher score have more free-radical-fighting ability.
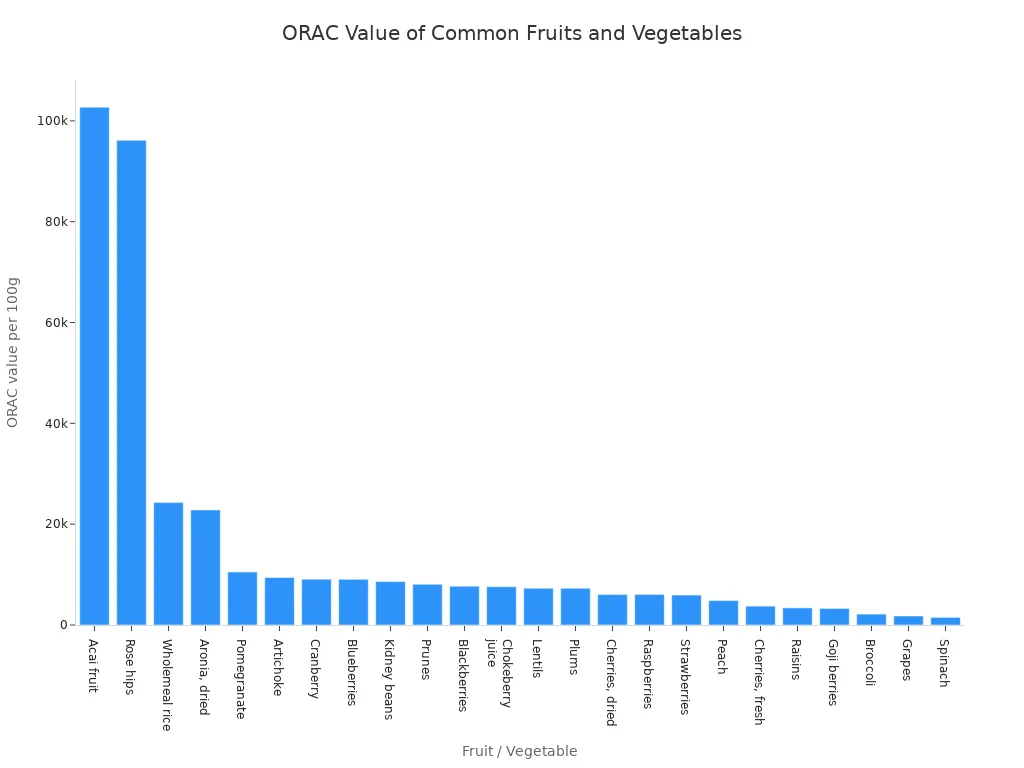
Some of the top antioxidant-rich foods include:
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries)
- Beans (small red beans, kidney beans)
- Dark leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Artichokes
- Dark chocolate (in moderation)
Including these foods in your meals is a delicious way to support your body’s defenses.
Antioxidants are essential nutrients for your health. They protect your cells by neutralizing harmful free radicals. This action helps reduce the risk of chronic diseases. While supplements are available, research shows they do not offer the same benefits as whole foods and can sometimes be harmful.
The most effective way to support your body is by eating a diverse diet. Fill your plate with colorful fruits, vegetables, and other plant-based foods to get a powerful mix of protective compounds. 🥦🍓🥕
FAQ
Can your body make its own antioxidants?
Yes, your body produces its own powerful antioxidants. One example is glutathione. However, the antioxidants you get from food, like vitamins C and E, provide extra support. This helps your body maintain a healthy balance and fight off excess free radicals.
Are antioxidant supplements a good idea?
Whole foods are the best source of antioxidants. Food contains a mix of nutrients that work together. High-dose supplements do not offer the same benefits. They can sometimes even cause harm. Always talk to a doctor before taking any new supplements.
What is the easiest way to get more antioxidants?
The easiest way is to eat a variety of colorful plants. Each color provides different types of antioxidants. Try to fill your plate with a rainbow of fruits and vegetables every day. This simple habit gives your body a powerful defense. 🥦
Do antioxidants stop all aging?
No, antioxidants cannot stop the natural aging process. They can, however, help slow down some signs of aging caused by free radical damage. This includes protecting your skin’s collagen and supporting brain health as you get older.
See Also
Alpha Lipoic Acid: Benefits and Its Role in Your Wellness Journey
Naxttii Health Vitamins: Understanding Their Efficacy and Time to Work
5-MTHF Supplement: Science-Backed Benefits for Enhanced Modern Wellness
Methylated Vitamins: Unlocking Optimal Absorption and Overall Wellness Benefits