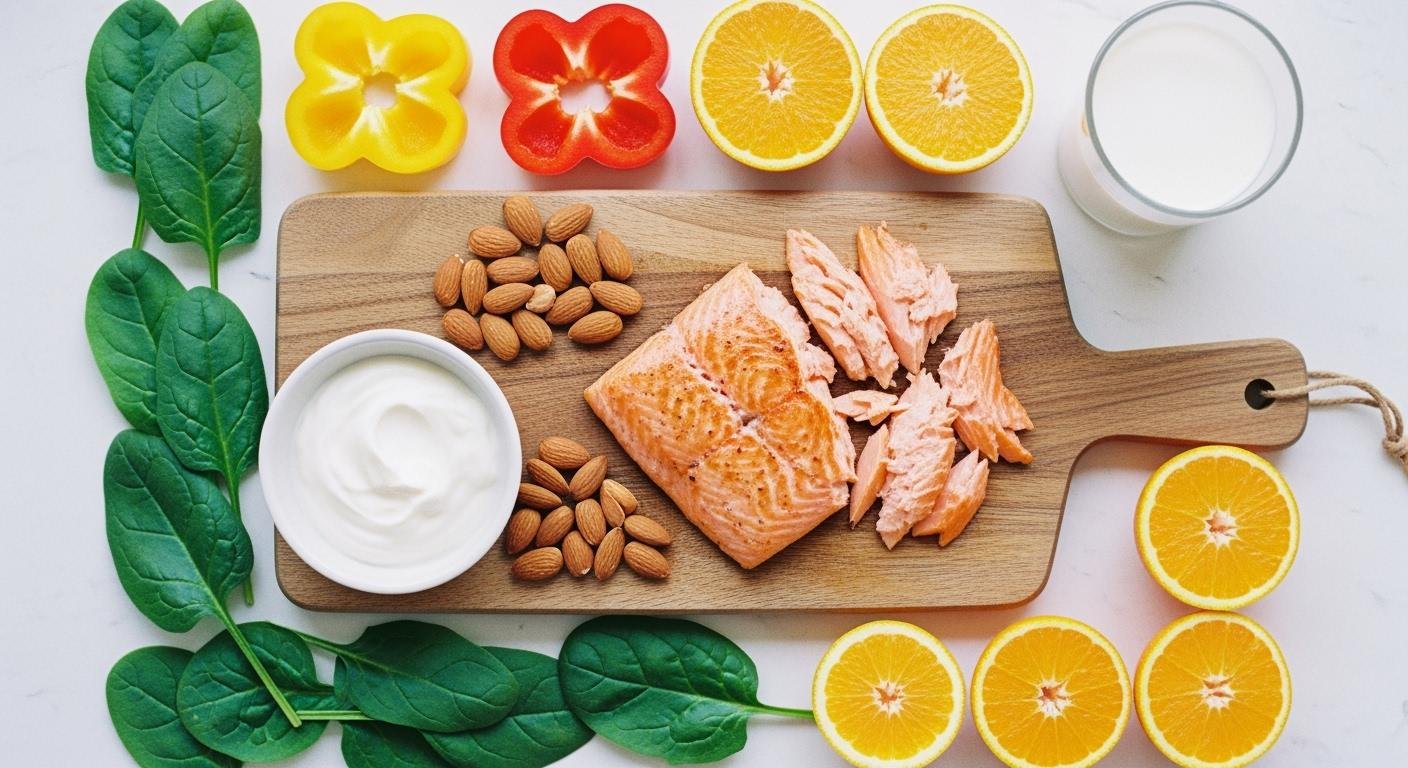
You might eat plenty of food, but your body could still be starving for essential micronutrients. Many American men face this issue. The typical Western diet often causes gaps in key nutrients. This list shows the most common nutrients men lack.
- Magnesium
- Vitamin D
- Potassium
- Fiber
- Omega-3s
- Zinc
Filling these nutritional gaps can boost your energy, strengthen your immune system, and support your heart health.
Key Nutrients Men Lack and Why It Matters
You might think a full stomach equals good nutrition. This is a common mistake. Understanding the difference between the food you eat and the nutrients you absorb is the first step toward better health. The nutrients men lack can have a big impact on daily life.
The Modern Diet Gap
The modern American diet often provides plenty of calories from processed foods, fats, and sugars. However, it frequently falls short on essential vitamins and minerals. Research shows that men are often more likely than women to have low levels of key micronutrients. These include magnesium, zinc, and several B vitamins. This gap happens because processed meals replace nutrient-dense whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Your body needs these micronutrients for almost every function, from producing energy to fighting off sickness.
Beyond Calories to Micronutrients
Focusing only on calories and macronutrients (protein, carbs, fat) is not enough. Micronutrients are the small but mighty players that keep your body running smoothly. Ignoring the key nutrients men lack can lead to noticeable problems over time. You might experience issues that you dismiss as normal aging or stress.
Are You Missing Key Nutrients?
Watch for these common signs of micronutrient deficiencies:
- Constant fatigue or muscle weakness
- Frequent muscle cramps, especially after activity
- Persistent joint pain
- Dry skin or brittle hair
- Sores in your mouth or on your tongue
- Trouble with concentration or memory
Ignoring these signals can lead to serious long-term health consequences. These include osteoporosis, a weaker immune system, and even cognitive decline. Paying attention to your micronutrient intake is a powerful investment in your long-term health and vitality.
Magnesium
Magnesium is a powerhouse mineral involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in your body. You need it for almost everything, yet many men do not get nearly enough. Studies show a large percentage of American men, with some estimates as high as 88%, consume less magnesium than recommended. This shortfall can impact your daily energy and long-term health.
Why Men Need Magnesium
Your body uses magnesium for critical jobs. It helps turn food into energy by assisting in the creation of ATP, your body’s main energy molecule. Without enough magnesium, your cells cannot produce energy efficiently, leaving you feeling tired. This mineral also plays a key role in muscle function. It acts as a natural calcium blocker, helping your muscle cells relax after contracting. A lack of magnesium can prevent this relaxation, leading to muscle tightness and cramps.
Our discovery can have a wide impact for understanding a variety of biological processes because the ATP molecule is involved in everything from muscle work and transport in and out of cells to bacterial infections.
Your daily magnesium needs depend on your age. You can check your recommended daily amount in the table below.
| Age Group (years) | Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) for Adult Men |
|---|---|
| 19–30 | 400 mg |
| 31+ | 420 mg |
Best Food Sources
You can easily increase your magnesium intake by adding certain foods to your diet. Focus on incorporating some of these nutrient-dense options into your weekly meals.
- Rice Bran: A single cup provides an impressive 922 mg.
- Tofu: One cup of tofu contains around 146 mg.
- Wheat Germ: An ounce of toasted wheat germ offers 91 mg.
- Alaskan King Crab: A single leg delivers about 84 mg.
- Peanut Butter: Two tablespoons of smooth peanut butter give you 57 mg.
Other great sources include leafy green vegetables like spinach, nuts like almonds and cashews, and seeds like pumpkin seeds.
Vitamin D

Vitamin D is often called the “sunshine vitamin” for a good reason. Your body produces it when your skin is exposed to sunlight. This nutrient is crucial for your overall health, yet a huge number of men do not get enough. A deficiency can affect your bones, immune system, and even your hormone levels.
The “Sunshine Vitamin”
Your body needs Vitamin D to absorb calcium, which is essential for strong bones. Without enough Vitamin D, you risk developing weak or brittle bones over time. This vitamin also plays a vital role in keeping your immune system ready to fight off illnesses.
For men, Vitamin D is particularly important for hormonal health. Research shows a connection between Vitamin D levels and testosterone production. Your body has Vitamin D receptors in the cells responsible for making testosterone. This suggests the vitamin is directly involved in regulating this key male hormone.
How Much Vitamin D Do You Need? ☀️
Your daily requirement for Vitamin D changes as you get older. Here are the general recommendations for adult men:
- Adults up to 70 years old: At least 600 IU (15 mcg) daily.
- Adults over 70 years old: At least 800 IU (20 mcg) daily.
How to Boost Your Levels
Getting enough direct sun exposure is the best way to produce Vitamin D. However, this is difficult for many people due to indoor jobs, northern climates, or the use of sunscreen. Food sources of Vitamin D are also quite limited, making it hard to meet your needs through diet alone.
For this reason, supplementation is often the most reliable strategy. If you have limited sun exposure, experts often recommend a daily intake of at least 2000 IU to maintain sufficient levels. You can also find Vitamin D in fortified foods and certain whole foods.
Consider adding these to your diet:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and tuna are excellent sources.
- Fortified Milk: Many dairy and plant-based milks have added Vitamin D.
- Egg Yolks: The yolk contains a small but helpful amount of Vitamin D.
- Fortified Cereals: Check the label on your breakfast cereal for added Vitamin D.
Potassium
Potassium is an essential mineral and electrolyte that your body needs to function correctly. It plays a huge role in everything from nerve signals to muscle contractions. Despite its importance, it is one of the most common nutrient shortfalls for men. In fact, studies show that approximately 95% of American men fail to consume the recommended amount.
The Sodium Balancer
You can think of potassium as the counterpart to sodium. A diet high in sodium, common in Western countries, can raise your blood pressure. Potassium helps counteract this effect. It signals your body to excrete more sodium through urine, which helps relax blood vessel walls and lower blood pressure.
This balancing act is crucial for your long-term cardiovascular health. Research consistently shows that adequate potassium intake is linked to better heart outcomes. Multiple studies have found that potassium supplementation can significantly reduce blood pressure and may lower the risk of stroke by as much as 24%.
Your Daily Potassium Target 🎯
The recommended daily intake for potassium is provided as an Adequate Intake (AI). This value is set to ensure you get enough for optimal health.
Age Group (years) Recommended Daily Intake (mg) 19–50 3,400 51+ 3,400
Potassium-Rich Foods
Hitting your daily potassium target is easier than you might think. You do not need to rely on supplements. You can find this mineral in many delicious and healthy whole foods. Try adding some of these options to your meals this week.
- Sweet Potato: A single cup of mashed sweet potato gives you about 16% of your daily potassium. It is also a great source of fiber and vitamin A.
- Avocado: One whole avocado provides nearly 15% of your daily need. It is also packed with healthy fats and is naturally low in sodium.
- Watermelon: Just two wedges of this refreshing fruit deliver almost 14% of your daily potassium, making it a perfect summer snack.
- Coconut Water: One cup contains 13% of your daily value. It is a great natural option for hydration and replenishing electrolytes after a workout.
- Spinach: This leafy green is a powerhouse. One cup of frozen spinach offers 12% of your daily potassium, along with vitamins A and K.
Fiber
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate your body cannot digest. It plays a critical role in your health, yet most men fall far short of getting enough. This creates a significant nutritional gap.
Importance for Gut and Heart Health
You need fiber for a healthy digestive system. It feeds the good bacteria in your gut and helps keep you regular. Beyond digestion, fiber is a powerful ally for your heart. Research shows that a high-fiber diet is linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease in men. One study found that men who ate more fiber had a lower risk of death from heart-related issues. Fiber helps by improving your body’s response to insulin and preventing cholesterol from being absorbed. These actions directly support a healthier heart.
How Much Fiber Do You Need? 🌾
Health guidelines recommend men aim for about 38 grams of fiber per day. Unfortunately, the average man consumes far less, creating a major deficiency.
Simple Ways to Get More Fiber
You do not need to overhaul your entire diet to increase your fiber intake. Small, simple swaps can make a big difference over time. Making these changes can help you easily reach your daily goal.
Try these easy food swaps to boost your fiber:
| Instead of This | Try This Instead | Fiber Boost |
|---|---|---|
| White Pasta (2 oz) | Chickpea Pasta (2 oz) | +3 grams |
| Potato Chips (1 oz) | Roasted Chickpeas (1 oz) | +5.2 grams |
| 1/2 Banana | 1/2 Avocado | +3.1 grams |
| Granola (1/4 cup) | Cacao Nibs (1 oz) | +7 grams |
Adding foods like beans, lentils, whole grains, and berries to your meals will also significantly increase your daily fiber.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Omega-3s are essential fatty acids that your body cannot make on its own. You must get them from your diet. They are powerful anti-inflammatory agents that play a key role in your overall health. The typical Western diet has an omega-6 to omega-3 ratio of around 16:1. For better health, you should aim for a ratio closer to 1:1, which was common in ancestral diets. An imbalance can lead to chronic inflammation, showing up as issues like joint pain or dry skin.
Benefits for Brain and Joints
Your brain and joints rely heavily on omega-3s to function optimally. Your brain is nearly 60% fat, and omega-3s are a major building block of brain cells. Research shows that a higher intake of these fats is linked to better brain health. For example, studies connect higher omega-3 levels with a larger hippocampus, the part of your brain vital for learning and memory. This can also improve your ability to understand complex ideas.
For your joints, omega-3s work by reducing the production of inflammatory substances in your body. This action helps soothe joint pain and stiffness. By lowering overall inflammation, you support not only your joints but also your heart health, reducing your risk for cardiovascular disease.
Top Food and Supplement Sources
You can boost your omega-3 levels through both food and supplements. Fatty fish are the best dietary source.
How Much Do You Need? 🐟 Health organizations recommend a minimum of 500 mg of combined EPA and DHA (the most important omega-3s) daily. Many adults find a supportive intake of 2000 to 3000 mg daily to be beneficial.
Adding fatty fish to your diet two times a week is a great strategy. The chart below shows some of the best fish sources.
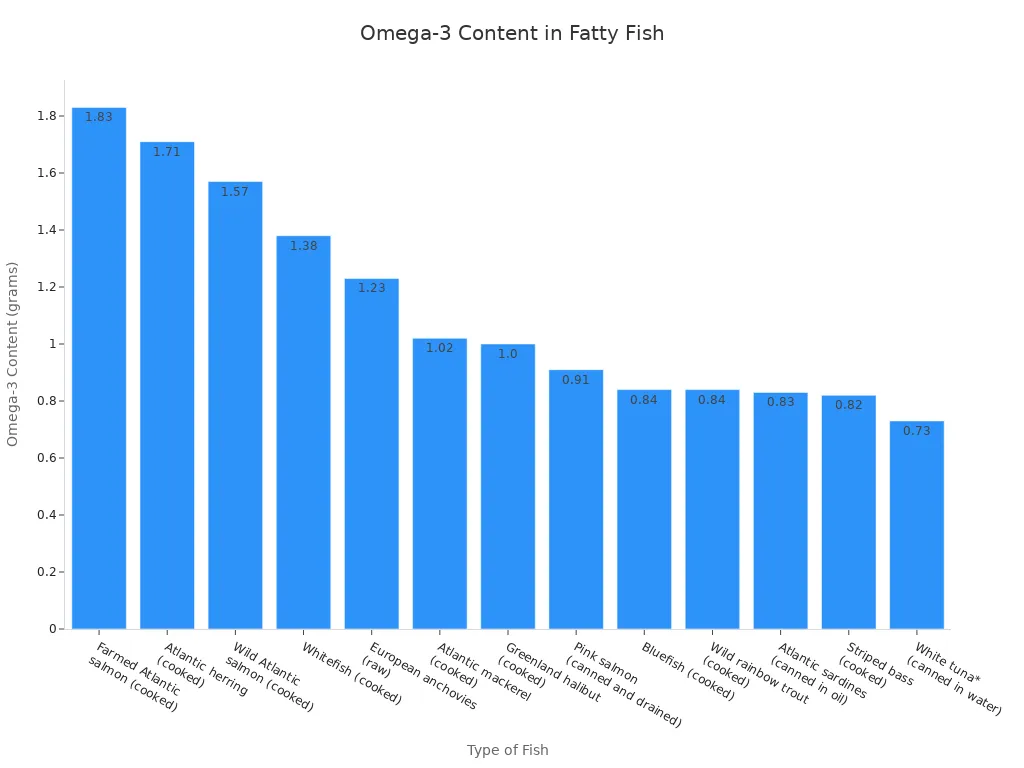
If you do not eat fish regularly, a high-quality fish oil or algae-based supplement is an effective way to ensure you get enough of these crucial fats.
Zinc
Zinc is a vital mineral that supports hundreds of important processes in your body. You need it for a strong immune system, proper wound healing, and healthy hormone levels. Despite its importance, an estimated 17% of the world’s population is at risk for not getting enough zinc. This deficiency is especially common in regions with limited access to animal-based foods.
Why Zinc is Crucial for Men
Your body depends on zinc for basic cellular functions, including cell division and protein creation. This mineral is a key player in your immune defense. It helps develop and activate your immune cells, such as T-cells and B-cells, which fight off infections. A lack of zinc can weaken your immune response.
For men, zinc is particularly critical for reproductive health and maintaining healthy testosterone levels. The mineral is directly involved in the production of testosterone. Research shows a clear link between low zinc status and reduced testosterone. A deficiency can lead to issues like impaired fertility and low libido.
Your Daily Zinc Target 🎯
The recommended daily allowance for zinc is straightforward for adult men.
Age Group (years) Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) 19+ 11 mg
Foods High in Zinc
You can easily meet your daily zinc needs by including certain foods in your diet. Animal products are particularly rich in this mineral, but many plant-based options are also excellent sources.
Here are some of the best foods to boost your zinc intake:
- Top Animal Sources:
- Shellfish (especially oysters)
- Beef
- Pork
- Poultry
- Top Plant-Based Sources:
- Chickpeas
- Lentils
- Hemp seeds
- Almonds
- Kidney beans
Adding a serving of beef, a handful of almonds, or a portion of lentils to your meals can help you hit your daily target and support your overall health.
You now know the key nutrients men lack: Magnesium, Vitamin D, Potassium, Fiber, Omega-3s, and Zinc. Filling the gaps for these common nutrients men lack does not require a difficult diet overhaul. You can make a big difference with small, strategic food choices. Adding items like fatty fish, leafy greens, nuts, and beans to your meals will boost your intake significantly.
Your Next Step 🚀
Start by adding one of these nutrient-rich foods to your meals this week. You can feel the difference.
FAQ
Can a multivitamin cover all these nutrients?
A multivitamin can help fill small gaps. However, many do not contain enough magnesium, potassium, or omega-3s. You should always prioritize getting nutrients from whole foods first. Food provides the best and most complete nutrition for your body.
Should I get a blood test for deficiencies?
You should talk to your doctor if you suspect a deficiency. Your doctor can review your symptoms and diet. They will decide if a blood test is necessary to confirm low levels of a specific nutrient like Vitamin D or zinc.
How long until I feel better after improving my diet?
You might notice more energy within a few weeks. Other benefits, like stronger bones or better heart health, build over months. Consistency is key. Stick with your new healthy habits to see the best long-term results.
Remember 💡 Every person’s body is different. Your results may vary based on your starting health and your specific dietary changes.
Do I need more of these nutrients if I am very active?
Yes, your needs often increase with exercise. You lose electrolytes like potassium through sweat. Your muscles also use more magnesium for recovery and energy. An active lifestyle requires you to pay closer attention to your nutrient intake for optimal performance.
See Also
Unlocking Wellness: The Science-Backed Advantages of 5-MTHF Supplementation
Top Vegan Joint Support: A Science-Driven Guide for Health-Conscious Choices
Magnesium Supplements: A Confident And Clear Starting Point For Beginners
Understanding ADHD And Protein: An Essential Introductory Guide For Beginners
Copper In Nutrition: Defining Its Health Roles And Supplementation Guidance